|
Common Name(s): Shortleaf Pine Scientific Name: Pinus echinata Distribution: Southeastern United States, though also widely grown on plantations Tree Size: 65-100 ft (20-30 m) tall, 2-3 ft (.6-1 m) trunk diameter Average Dried Weight: 35 lbs/ft3 (570 kg/m3) Specific Gravity (Basic, 12% MC): .47, .57 Janka Hardness: 690 lbf (3,070 N) Modulus of Rupture: 13,100 lbf/in2 (90.3 MPa) Elastic Modulus: 1,750,000 lbf/in2 (12.10 GPa) Crushing Strength: 7,270 lbf/in2 (50.1 MPa) Shrinkage: Radial: 4.6%, Tangential: 7.7%, Volumetric: 12.3%, T/R Ratio: 1.7 |
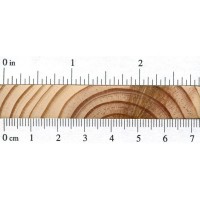
Color/Appearance: Heartwood is reddish brown, sapwood is yellowish white.
Grain/Texture: Straight grained with a fine to medium texture.
Endgrain: Large resin canals, numerous and evenly distributed, mostly solitary ; earlywood to latewood transition abrupt, color contrast high; tracheid diameter medium-large.
Rot Resistance: The heartwood is rated as moderate to low in decay resistance.
Workability: Overall, Shortleaf Pine works fairly well with most tools, though the resin can gum up tools and clog sandpaper. It has a moderate dulling effect on cutting edges. Shortleaf Pine glues and finishes well.
Odor: Has a distinct smell that is shared among most species in the Pinus genus.
Allergies/Toxicity: Working with pine has been reported to cause allergic skin reactions and/or asthma-like symptoms in some people. See the articles Wood Allergies and Toxicity and Wood Dust Safety for more information.
Pricing/Availability: Should be widely available as construction lumber for a modest price.
Sustainability: This wood species is not listed in the CITES Appendices, and is reported by the IUCN as being a species of least concern.
Common Uses: Shortleaf Pine is used for heavy construction, such as: bridges, beams, poles, railroad ties, etc. It’s also used for making plywood, wood pulp, and veneers.
Comments: Shortleaf Pine is considered to be in the group of southern yellow pines, and shares many characteristics with other species of this group (Longleaf, Slash, and Loblolly Pine) such as being: hard, dense, and possessing an excellent strength-to-weight ratio.
- Austrian Pine (Pinus nigra)
- Caribbean Pine (Pinus caribaea)
- Eastern White Pine (Pinus strobus)
- Jack Pine (Pinus banksiana)
- Jeffrey Pine (Pinus jeffreyi)
- Khasi Pine (Pinus kesiya)
- Limber Pine (Pinus flexilis)
- Loblolly Pine (Pinus taeda)
- Lodgepole Pine (Pinus contorta)
- Longleaf Pine (Pinus palustris)
- Maritime Pine (Pinus pinaster)
- Ocote Pine (Pinus oocarpa)
- Patula Pine (Pinus patula)
- Pinyon Pine (Pinus edulis)
- Pitch Pine (Pinus rigida)
- Pond Pine (Pinus serotina)
- Ponderosa Pine (Pinus ponderosa)
- Radiata Pine (Pinus radiata)
- Red Pine (Pinus resinosa)
- Sand Pine (Pinus clausa)
- Scots Pine (Pinus sylvestris)
- Slash Pine (Pinus elliottii)
- Spruce Pine (Pinus glabra)
- Sugar Pine (Pinus lambertiana)
- Sumatran Pine (Pinus merkusii)
- Table Mountain Pine (Pinus pungens)
- Western White Pine (Pinus monticola)
- Virginia Pine (Pinus virginiana)