
|
Common Name(s): Rock Elm, Cork Elm Scientific Name: Ulmus thomasii Distribution: Midwestern United States Tree Size: 65-100 ft (20-30 m) tall, 2-4 ft (.6-1.2 m) trunk diameter Average Dried Weight: 47 lbs/ft3 (755 kg/m3) Specific Gravity (Basic, 12% MC): .57, .75 Janka Hardness: 1,320 lbf (5,870 N) Modulus of Rupture: 14,800 lbf/in2 (102.1 MPa) Elastic Modulus: 1,540,000 lbf/in2 (10.62 GPa) Crushing Strength: 7,050 lbf/in2 (48.6 MPa) Shrinkage: Radial: 4.8%, Tangential: 8.1%, Volumetric: 14.9%, T/R Ratio: 1.7 |
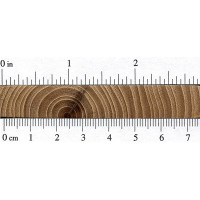
Color/Appearance: Heartwood is light to medium reddish brown. Paler sapwood is usually well defined.
Grain/Texture: Grain is interlocked (making it very resistant to splitting). With a somewhat coarse, uneven texture.
Rot Resistance: Rated as non-durable; susceptible to insect attack. Living trees are susceptible to Dutch elm disease.
Workability: Can be a challenge to work because of interlocked grain, especially on quartersawn surfaces. Planing can cause tearout and/or fuzzy surfaces. Poor dimensional stability. Glues, stains, and finishes well. Responds well to steam bending, and holds nails and screws well.
Odor: Elm usually has a strong, unpleasant smell when green; though once dried has very little odor.
Allergies/Toxicity: Although severe reactions are quite uncommon, Elm in the Ulmus genus has been reported as a sensitizer. Usually most common reactions simply include eye and skin irritation. See the articles Wood Allergies and Toxicity and Wood Dust Safety for more information.
Pricing/Availability: Should be moderately priced, though availability from mature trees has been greatly diminished by Dutch elm disease.
Sustainability: This wood species is not listed in the CITES Appendices or on the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.
Common Uses: Boxes, baskets, furniture, hockey sticks, veneer, wood pulp, and papermaking.
Comments: Elm trees are commonly infected with Dutch elm disease, a fungal disease spread by elm bark beetles. D.E.D. has wiped out millions of Elm trees worldwide.







I’ve got a fairly large slab of this waiting on an idea right now. 8’ x 5” and 28-32 in width. Fairly significant spalting as well. Honestly seems comparable to hard maple janka wise. Wish this was more readily available for furniture. It takes a French polish beautifully.
At our charity, Paddle Steamer Maid of the Loch on Loch Lomond, Scotland we have 3 old paddles measuring about 3metres long by 1 metres wide, thickness about 7cm – made up of 4 equal size planks. Some areas rotten but underneath good condition, very dense. We want to auction them off as we need to completely replace but need to know a reasonable price to ask. Can you advise us?
this elm, one of three (red and white (Amercian elm) is very rare in Québec, 2500 trees still remains, he have a status by the the government
I have found specimens of some tree standing but dead, even free of bark, long dead, but completely free on rot, even when found on the ground. Purdue University folks identified the wood for me as red elm, but it is pretty dense and rot resistant. Would that likely be rock elm?
It is. Rock elm is hotter and better for firewood
you’ll need a splitter. Rock elm doesn’t last
when split and stacked as good as red elm
Did you see this article on telling elms apart? https://www.wood-database.com/wood-articles/elm-wood-hard-and-soft/
Basically, if the growth rings have two to four rows of pores, it’s a soft elm like red elm. But if it has only a single row of pores at each growth ring, it’s a hard elm like rock elm.
But there’s also a lot of hybrids floating around out there because of Dutch elm disease and the need to have disease resistant hybrids, so in practical terms, you may not know what you’re dealing with, as different hybrids can take on different characteristics of either parent.